What is AWS IAM, How to Use It, Its Limitations, Pros and Cons, Best Practices
Introduction
As more and more businesses are moving their applications and data to the cloud, the importance of managing access to those resources has become crucial. AWS IAM (Identity and Access Management) is a service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that enables you to manage access to AWS services and resources securely. This article will cover the basics of AWS IAM, how to use it, its limitations, pros and cons, and best practices for using it effectively.
What is AWS IAM?
AWS IAM is a web service that allows you to manage access to AWS services and resources securely. With AWS IAM, you can create and manage AWS users and groups, and you can use permissions to allow or deny access to AWS resources. You can also use IAM to manage roles and policies, which define the actions that users, groups, and roles can perform on AWS resources.
How to Use AWS IAM
To use AWS IAM, you need to have an AWS account. Once you have an account, you can create IAM users, groups, and roles, and you can assign permissions to those entities.
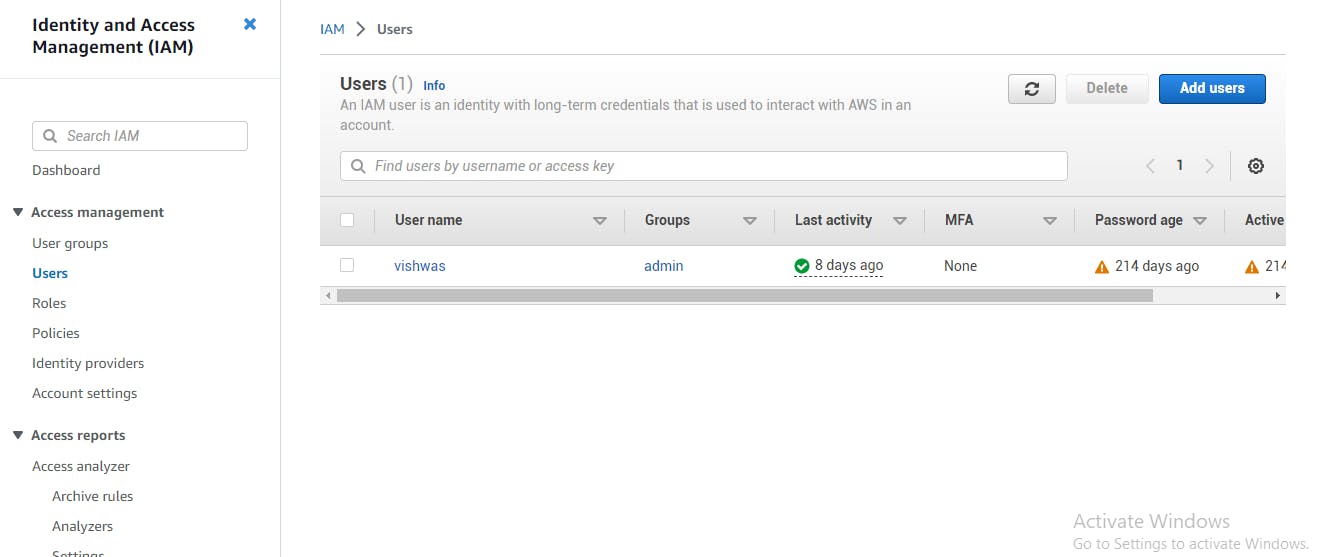
Creating IAM Users
To create an IAM user, you need to do the following:
Log in to your AWS account.
Open the IAM console.
Click on the "Users" link.
Click on the "Add user" button.
Enter the user's name and select the access type.
Create a password for the user or generate a password.
Add the user to one or more groups.
Click on the "Create user" button.
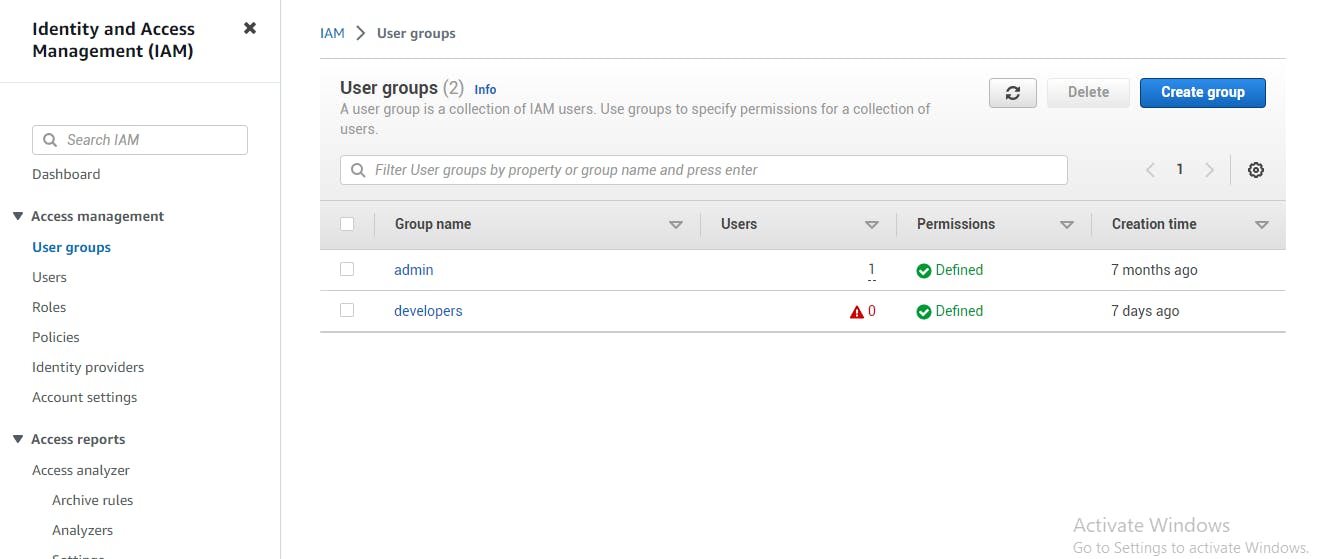
Creating IAM Groups
To create an IAM group, you need to do the following:
Log in to your AWS account.
Open the IAM console.
Click on the "Groups" link.
Click on the "Create group" button.
Enter a name for the group.
Add one or more policies to the group.
Click on the "Create group" button.
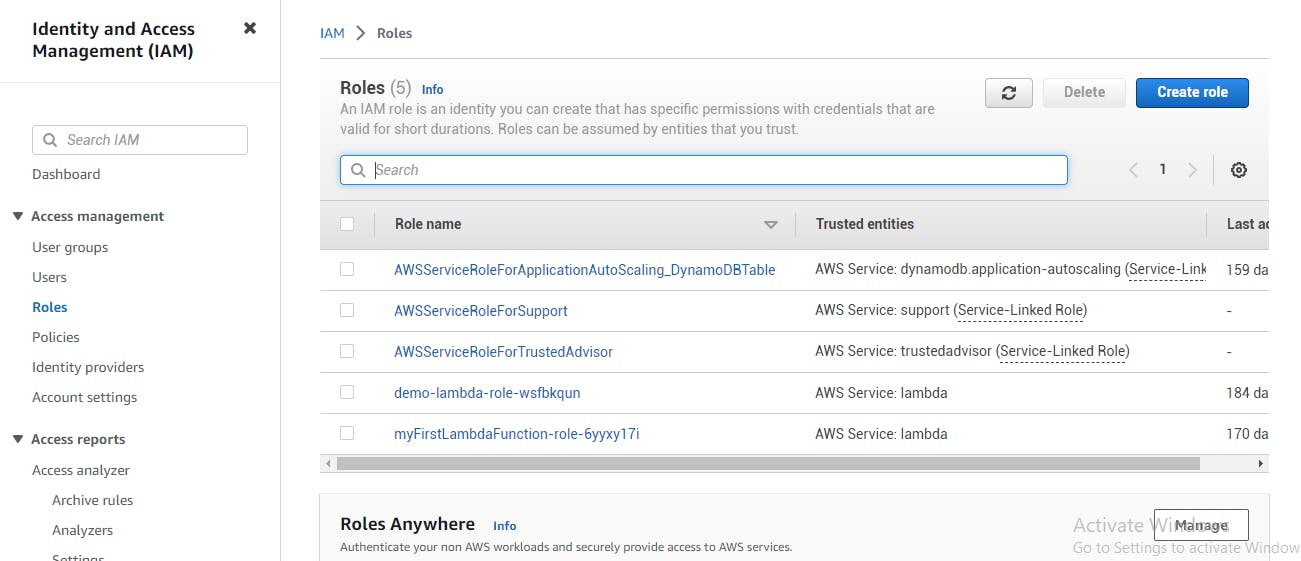
Creating IAM Roles
To create an IAM role, you need to do the following:
Log in to your AWS account.
Open the IAM console.
Click on the "Roles" link.
Click on the "Create role" button.
Select the type of trusted entity for the role.
Choose the permissions that the role should have.
Add tags to the role if needed.
Click on the "Create role" button.
Limitations of AWS IAM
While AWS IAM is a powerful service, it has some limitations that you need to be aware of.
Limited to AWS Resources
AWS IAM only manages access to AWS resources, so it does not manage access to resources outside of AWS. If you need to manage access to resources outside of AWS, you will need to use a different service.
Limited to Access Control
AWS IAM only manages access control, so it does not manage authentication. If you need to manage authentication, you will need to use a different service.
No Native Support for Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
While you can enable MFA for AWS IAM users, AWS IAM does not provide native support for MFA. You will need to use a separate service or a third-party tool to enable MFA.
Pros and Cons of AWS IAM
Like any service, AWS IAM has its pros and cons.
Pros
Provides a centralized location to manage access to AWS resources
Enables you to create and manage IAM users, groups, and roles
Allows you to define permissions for users, groups, and roles
Provides detailed logging of user activity
Cons
Limited to managing access to AWS resources
No native support for multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Complex to set up and manage for larger organizations
Best Practices for Using AWS IAM
To make the most of AWS IAM, it is important to follow some best practices.
Use Roles Instead of Users
Instead of creating IAM users for every individual, it is recommended to create roles and assign permissions to the roles. This makes it easier to manage access for larger organizations.
Use Groups to Manage Permissions
To simplify the management of permissions, it is recommended to use groups to manage permissions. You can assign permissions to a group and add users to the group.
Use Policy Conditions
Policy conditions allow you to add additional security controls to your policies. For example, you can add conditions that require MFA to be enabled or that limit access to specific IP addresses.
Enable MFA for Administrators
It is highly recommended to enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all administrators. MFA provides an additional layer of security to your AWS account.
Use IAM Roles for EC2 Instances
Instead of using access keys for EC2 instances, it is recommended to use IAM roles. IAM roles allow you to assign permissions to an EC2 instance, so you don't need to manage access keys.
Conclusion
AWS IAM is an essential service for managing access to AWS resources securely. By following best practices, you can use AWS IAM effectively and minimize the risk of unauthorized access to your resources.
FAQs
Is AWS IAM free to use?
Yes, AWS IAM is a free service. However, you may incur charges if you use other AWS services with IAM.
Can I use AWS IAM to manage access to resources outside of AWS?
No, AWS IAM only manages access to AWS resources.
Does AWS IAM provide native support for multi-factor authentication (MFA)?
No, AWS IAM does not provide native support for MFA. You will need to use a separate service or a third-party tool to enable MFA.
Can I use IAM roles for EC2 instances?
Yes, it is recommended to use IAM roles for EC2 instances instead of access keys.
Is AWS IAM difficult to set up and manage?
While AWS IAM can be complex to set up and manage for larger organizations, following best practices can make it easier to manage access to AWS resources.
By Vishwas Acharya 😉
Checkout my other content as well:
YouTube:
Podcast:
